The discovery of vitamin A by McCollum and Davis in 1913 ushered in the era of accessory food substances culminating in the achievement of that goal. It included the discovery of vitamin D and its production in skin caused by ultraviolet light. In our pervious blogs we have discussed about thyroid, but there is one more thing that we can’t deny that is deficiency of vitamin-D.
Today we are going to talk about covid and vitamin-D and its deficiency. Vitamin D deficiency is very common nowadays; it is estimated that about 1 billion people worldwide have low blood levels of the vitamin-D. Before moving forward, let’s understand vitamin D.

What is vitamin D?
Vitamin-D is more than a vitamin due its many receptors in the body. It should ideally be considered as a fat-soluble steroid hormone.
You may also know it as “vitamin of sun”, our bodies are unable to produce vitamin D on its own until it is expose to the sunlight. When exposed directly to the sunlight 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin absorbs UV B radiation and is converted to cholecalciferol.
Vitamin D is metabolized sequentially in the liver and kidneys into 25-hydroxyvitamin D which is a major circulating form and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D which is the biologically active form which is also known as calcitriol. Calcitriol is used to treat and prevent calcium maintenance homeostasis, for bone health and for preventing falls and fractures, in patients whose kidneys or parathyroid glands are not working normally.

What are the functions of vitamin D??
Calcium is requires, Phosphorus, magnesium and vitamin D in the right levels to successfully carry out its vital roles. Most common function is associated with bone health and calcium absorption, but it also helps in regulating enzymes in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid that are involved in manufacturing neurotransmitters and stimulating nerve growth. It also protects neurons from damaging effects of free radicals and reduces inflammation which otherwise can cause auto-immune diseases.
Adequate amount of vitamin D is needed by the adrenal glands to help regulate an enzyme necessary for the production of dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine. Some critical brain hormones that play major role in mood, stress management, and energy. Thus, a low vitamin D can contribute to depression and fatigue.
Vitamin D helps to maintain calcium levels in the bones and blood by:
- Increasing intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphorus
- Stimulating calcium deposition in the bones
- Reducing calcium and phosphorus excretion from the kidney
How about covid situation?
Low vitamin D levels have been associated with an increase in inflammatory cytokines and a significant risk of pneumonia, viral and infections in upper respiratory tract. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increase in thrombotic episodes, which are frequently observed in COVID-19.
Vitamin D deficiency has been found to occur more frequently in patients with obesity and diabetes. These conditions are reported to carry a higher mortality in COVID-19. If vitamin D does in fact reduce the severity of COVID-19 in regard to pneumonia/ARDS, inflammation, inflammatory cytokines and thrombosis, severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (SARS-CoV-2), myocarditis, microvascular thrombosis and/or cytokine storms, all of which involve underlying inflammation.
Can vitamin D help?
According to the National Institutes of Health and the World Health Organization.
Several recent studies have looked at the impact of vitamin D on COVID-19. One study of 489 people found that those who had a vitamin D deficiency were more likely to test positive for the virus that causes COVID-19 than people who had normal levels of vitamin D.
Other research has observed high rates of vitamin D deficiency in people with COVID-19 who experienced acute respiratory failure. These people had a significantly higher risk of dying.

Signs and symptoms of vitamin D deficiency :
- Getting sick and infections more often
- Fatigue and tieredness
- Bone and back pain
- Slow or impaired healing of wounds
- Bone, hair and muscle loss
- Depression and anxiety
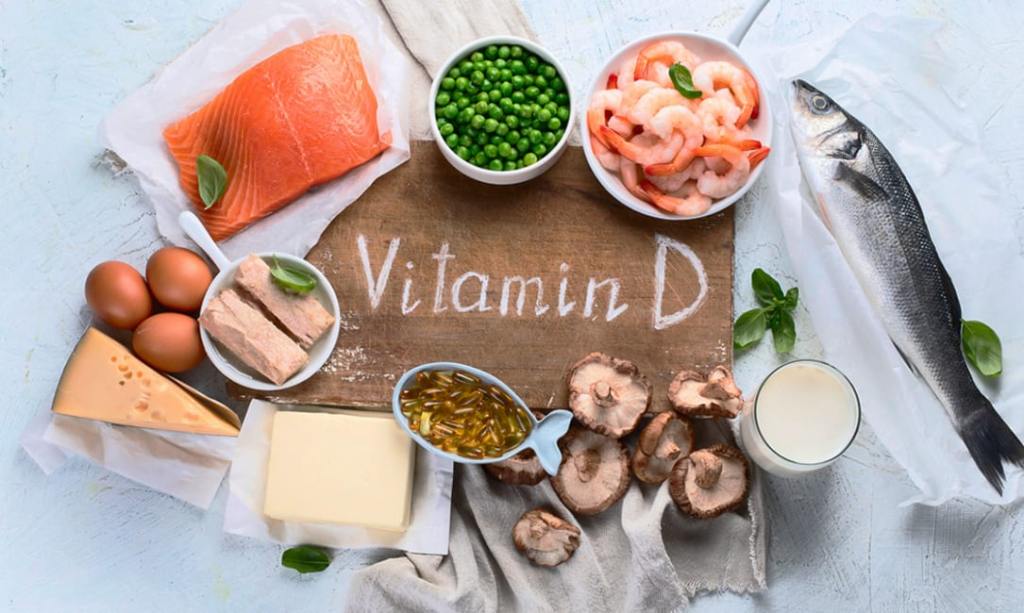
Food items to get optimum help??
- Fatty fish, like tuna, mackerel, and salmon
- Beef liver
- Cheese
- Egg yolks
- Butter
- Milk

But, but, but… wait, how much to be consumed??
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnancy | Lactation |
| 0-12 months* | 10 mcg (400 IU) | 10 mcg (400 IU) | ||
| 1–13 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | ||
| 14–18 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
| 19–50 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
| 51–70 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | ||
| >70 years | 20 mcg (800 IU) | 20 mcg (800 IU) |
Hope, you may found it helpfull and informative i would like to cover more and give you more health and fitness tips and tricks to fight and stay healthy against auto-immune diseases.

Very helpful 🙂👍 Thankyou for keeping it short and informative.💜
LikeLike
Thanks for guiding as always
Well written
All the best👍
LikeLike
Thanks for providing such helpful information.
Keep it Up!
LikeLike